| Meter Resistance | ||||
| The d-c resistance of a milliameter or | ||||
| voltmeter movement may be determined as follows: |
||||
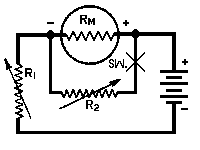 |
||||
| 1. | Connect the meter in series with a suitable battery and variable resist- ance R1 as shown in the diagram above. |
|||
| 2. | Vary R1 until a full scale reading is obtained. |
|||
| 3. | Connect another variable resistor R1 across the meter and vary its value until a half scale reading is obtained. |
|||
| 4. | Disconnect R2 from the circuit and measure its d-c resistance. |
|||
| The meter resistance RM is equal to the | ||||
| measured resistance of R2. | ||||
| Caution: Be sure that R1 has sufficient | ||||
| resistance to prevent an off scale reading of the meter. The correct value depends upon the sensitivity of meter, and voltage of the battery. The following formula can be used if the full scale current of the meter is known: |
||||
| R1 | = | voltage of the battery used | ||
|
|
||||
| full scale current of meter in amperes | ||||
| For safe results, use twice the value com- puted. Also, never attempt to measure the resistance of a meter with an ohmeter. To do so would in all proability result in a burned-out or severly damaged meter, since the current required for the operation of some ohmeters and bridges is far in excess of the full scale current required by the movement of the average meter you may be checking. |
||||
| Ohms per Volt Rating of a Voltmeter | |||||
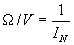 |
|||||
| Where: |  |
= | ohms per volt, | ||
| Ifs | = | full scale current in amperes. | |||
 |
|||||
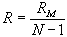 |
|||||
| R | = | shunt value in ohms, | |||
| N | = | the new full scale reading divided | |||
| by the original full scale reading, both being stated in the same units, |
|||||
| RM | = | meter resistance in ohms | |||
| Multi-Range Shunts | |||||
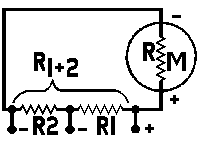 |
|||||
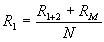 |
|||||
| R1 | = | intermediate or tapped shunt value | |||
| in ohms, | |||||
| R1+2 | = | total resistance required for the low- | |||
| est scale reading wanted, | |||||
| RM | = | meter resistance in ohms, | |||
| N | = | the new full scale reading divided | |||
| by the original full scale reading, both being stated in the same units, |
|||||
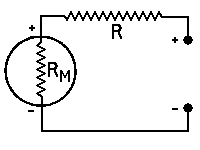
| Voltage Multipliers | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
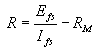 |
||||||||
| R | = | multiplier resistance in ohms, | ||||||
| Efs | = | full scale reading required in volts, | ||||||
| Ifs | = | full scale current of meter in am- | ||||||
| peres, | ||||||||
| RM | = | meter resistance in ohms | ||||||
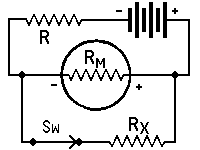
| Measuring Resistance | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
| with Milliammeter and battery* | ||||||||
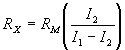 |
||||||||
| RX | = | unknown resistance in ohms, | ||||||
| RM | = | meter resistance in ohms, or effec- | ||||||
| tive meter resistance if a shunted range is used, |
||||||||
| I1 | = | current reading with switch open, | ||||||
| I2 | = | current reading with switch closed, | ||||||
| RL | = | current limiting resistor of suffi- | ||||||
| cient value to keep meter reading on scale when switch is open |
||||||||
| *Approximately true only when current limiting resistor is large as compared to meter resistance. |
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
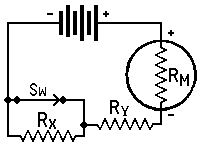
| Measuring Resistance–(Continued) | ||||||||
 |
||||||||
| with Milliammeter, Battery and Known Resistor | ||||||||
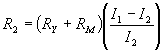 |
||||||||
| RX | = | unkown resistance in ohms, | ||||||
| RY | = | kown resistance in ohms, | ||||||
| RM | = | meter resistance in ohms, | ||||||
| I1 | = | current reading with switch closed, | ||||||
| I2 | = | current reading with switch open, | ||||||
 |
||||||||
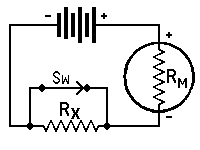
| with voltmeter and Battery | ||||||||
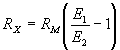 |
||||||||
| RX | = | unkown resistance in ohms, | ||||||
| RM | = | meter resistance in ohms, including | ||||||
| multiplier resistance if a multiplied range is used, |
||||||||
| E1 | = | voltmeter reading with switch closed, | ||||||
| E2 | = | voltmeter reading with switch open, | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
