| Metric Relationships | |||||||
 |
|||||||
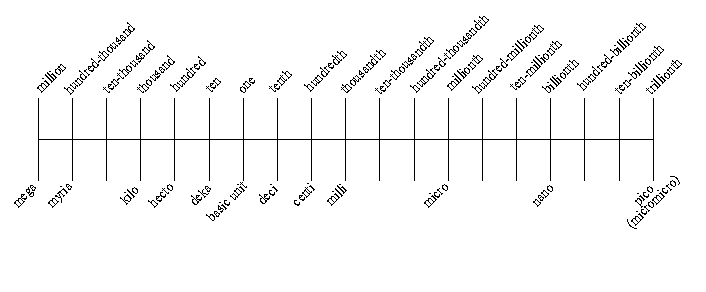
| The above chart shows the relation of | term watt is a basic unit). The number of | ||||||
| the most used values in the American and the metric systems of notation. |
steps so counted is three, and the direction was to the left. Therefore, 5.0 milliwatts is |
||||||
| the equivalent of .005 watts. | |||||||
| This chart also serves to quickly locate | |||||||
| the decimal point in the conversion from one metric expression to another. Example: Convert 5.0 milliwatts to watts. |
Example: Convert 0.00035 microfarads to picofarads (micromicrofarads). Here the number of steps counted will be six to the right. Therefore 0.00035 microfarads is the equivalent of 350 picofarads. |
||||||
| New International Codes | |||||||
| The gradual adoption in this country of | 2. | “Kilomega” (km) has been replaced | |||||
| new international codes for metric prefixes | by “giga” (G). | ||||||
| amd measurement terminology by govern- | “Hertz”. This term was recently adopted | ||||||
| ment agencies, industry, technical maga- zines, book publishers and others, is slowly changing the system of measurement and evaluation codes in general use today. |
in the United States but it is not represented in this handbook. It is, however, already used by some publishers in place of”cycles” in references to frequency specifications. |
||||||
| The old familiar terms such as “cycles” | |||||||
| (cyc), “kilocycles” (kc) and “megacycles” | |||||||
| Acceptance of the new codes here, how- | (Mc), are replaced by “Hertz” (Hz), | ||||||
| ever, has been slow. We have , therefore, continued to use the more familial termi- nology in this handbook with the following exceptions which appear in the metric |
“kilohertz” (kHz) and “megahertz” (MHz). |
||||||
| To combine two of these changes in one | |||||||
| tables in the next two pages: | specification, the old term “kilomegacycles” (kMc) has become “gigahertz” (GHz). |
||||||
| 1. | The cumbersome term “micromicro” has been replaced by “pico”. Micro- microfarad” (µµf) now becomes “pico- farad” (pf). |
Heinrich Rudolph Hertz, was born in | |||||
| Germany in 1857 and died in 1894. He was the first scientist to dect, create and measure electromagnetic waves. |
|||||||
